5368+ reviews
Order by 16:00 for same day shipping
14 days return
DE
EN
Individual
Business

21/10/2025
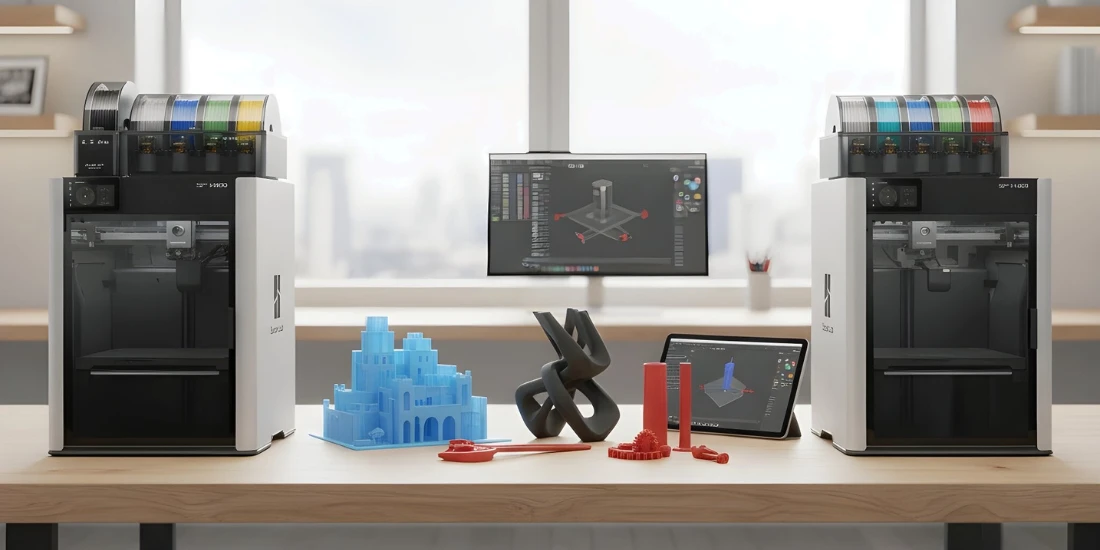
What is 3D Printing? Everything you need to know about this technology.
Introduction
Once futuristic, 3D printing is now a powerful tool. It is changing the way we design and manufacture. From art to medical devices, the possibilities are endless. This process builds ideas layer by layer, making complex shapes easy to realize.
In this guide, you will learn all about 3D printing. We will discuss how it works, what printers and materials are available, and how to get started. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced maker, you will find practical insights and inspiration here.
Want to print your own designs? Or modify existing models? 3D printing brings ideas to life. Use it for prototypes, functional parts or creative projects. The technology is growing rapidly and is becoming more accessible.
Dive into the world of 3D printing and discover what you can create!
What is 3D printing?
3D printing builds objects layer by layer from a digital design. It adds material instead of removing it. This makes it more efficient than old methods like carving or casting.
The process is precise and suitable for complex shapes. Many materials are possible, such as plastic, metal and ceramic. Because little waste is created, 3D printing is sustainable.
The technology enables customization in various sectors. In aviation, it helps to make lighter, stronger components. In the medical world, prostheses and implants are custom printed. Consumer products, such as jewelry and furniture, also benefit from this flexibility.
3D printing accelerates innovation. Designers quickly create prototypes and test new ideas. Companies save time and money by producing directly from a digital file.
The technology continues to grow and become more accessible, opening up new opportunities for industries and individuals. In the future, 3D printing could play a bigger role in manufacturing, sustainability and creativity.
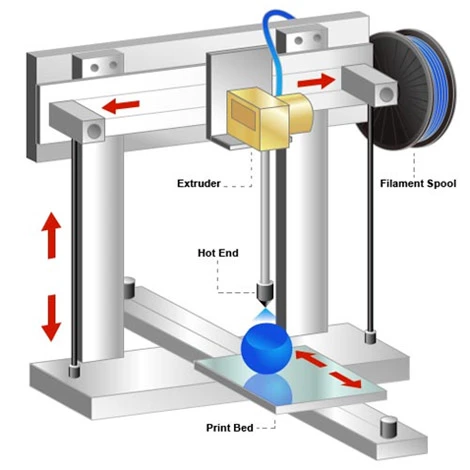
How does a 3D printer work?
3D printing is a technique that converts digital designs into tangible objects. The process starts with a 3D model , which you design yourself in CAD software or download from an online platform. Many websites offer ready-made models, both free and paid.
After designing, you save the model as an .STL or .OBJ file . You then use slicing software to divide the model into layers. This process is called slicing . The slicer converts the model into instructions that the printer can understand.
The four steps of 3D printing
- Design Create a model with CAD software or download an existing design. Popular websites like Thingiverse and Makerworld offer thousands of models.
- Slicing Software such as Bambu Studio or Cura slices the model into layers and sets important parameters. Think of print speed, layer height and temperature.
- Printing The printer heats and melts the material. Then it builds the object layer by layer. This can take from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the size and settings.
- Finishing After printing, remove support structures. You can sand, polish or paint the object for a smooth and professional result.
Settings and optimization
A smaller layer height gives a more detailed print, but increases the print time. Larger layers are faster, but less refined.
Many beginners use default settings , which often give good results. Experienced users adjust settings to further improve print quality.
Thanks to user-friendly software and online resources, 3D printing is more accessible than ever , for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Reducing the seam of a 3D print
During printing a seam is created where the layers meet. This is especially visible on round objects. In Bambu Studio you see the seam as a white line after slicing.
You can adjust the seam settings to make them less visible:
- Back : Place the seam in a fixed, less visible place.
- Closest : Distributes the seam evenly over the model for a neater finish.
By choosing these settings wisely, you can improve the appearance of your print without additional post-processing.
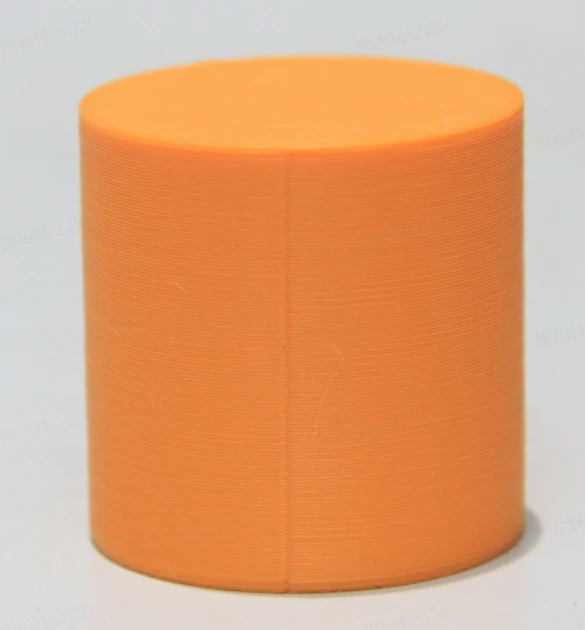

Ironing: Creating a smooth surface
For objects with a flat top, such as a cylinder, it can be nicer to iron the top layer smooth. Ironing ensures that the top of the print is even.
This is how it works:
- After printing the top layer, the filament is briefly removed from the print head.
- The print head cools down slightly, which keeps the filament softer but does not melt.
- The print head then moves over the top and smooths it out.
This feature can also be applied to multiple top surfaces for a smooth finish.
Walls: Adding extra strength
Want a sturdier object? Then walls is a setting you can adjust.
- This determines the number of outer walls of the print.
- Exterior walls are the strongest parts of the object.
- Adjust this setting in combination with thin padding for best results.
Thin filling (infill): Determine firmness and weight
FDM printers never print objects solid. Instead, they use infill , an internal structure with various patterns.
- The standard grid pattern is not always the best option.
- With a grid, the printer first lays down parallel lines in one direction and then in the other. This can cause the print head to hit previous lines and knock the print over.
- A better choice is the gyroid pattern .
- This pattern places the lines in one direction per layer.
- The next layer is laid in the opposite direction.
- This provides greater strength, safety and speed.
The infill also affects the weight and density of the object.
- Higher infill percentage → Stronger and heavier.
- Lower infill percentage → Lighter and less filament usage.
Support: Support for overhanging parts
FDM printers build a model layer by layer. They cannot print in the air .
- Support adds temporary support structures to the model.
- This prevents overhanging parts from sinking or deforming.
- The top layer of the support is printed in such a way that it breaks easily and is simple to remove.
Experience and optimization
Every print requires different settings. As you gain experience, it will become easier to make the right choices. In the beginning, settings may not be perfect right away. By experimenting and making adjustments, you will learn what works best for your printer and filament.
Types of 3D printers
There are different types of 3D printers, each with unique technologies and applications.
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers
- Usage: Widely used by hobbyists, makers and professionals for product design and prototyping.
- Materials: PLA, ABS, PETG and other thermoplastics. Each material has unique properties such as strength or flexibility.
- Advantages: Affordable, simple and versatile. Suitable for home and small business use. Little technical knowledge required.
- Disadvantages: Lower resolution than other 3D printing techniques. Prints may have visible layer lines and require additional post-processing.
- Example: The Bambu Lab X1 Carbon Combo offers fast, accurate prints and supports multi-color printing.
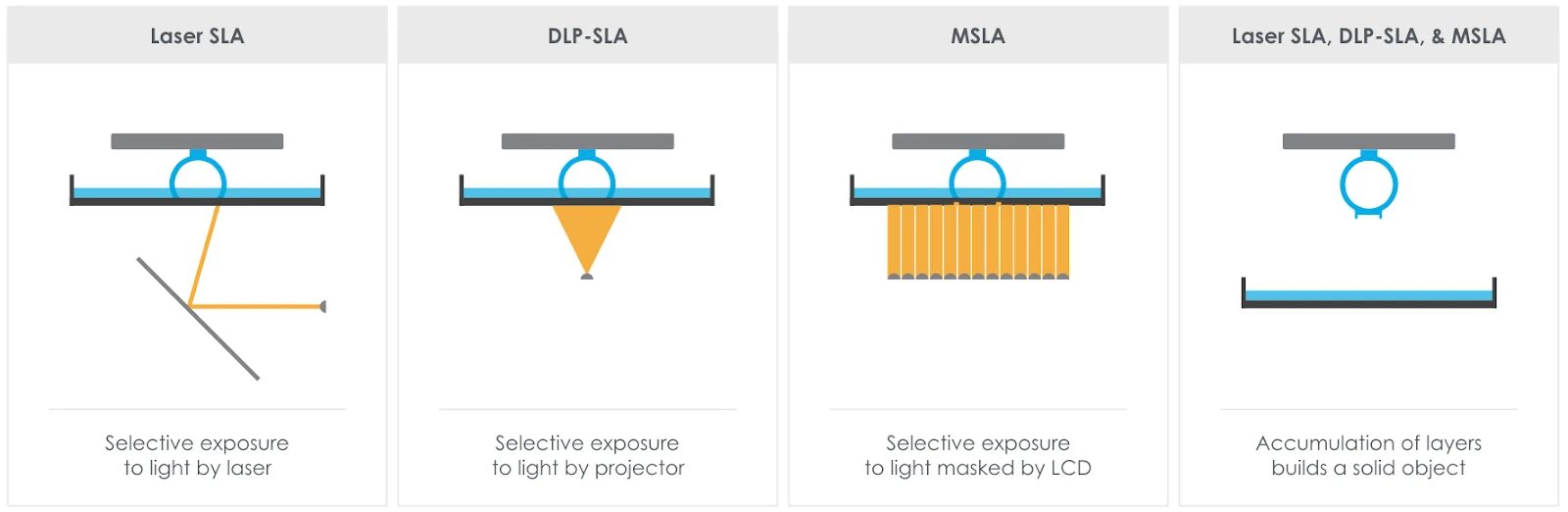
SLA/DLP printers (Stereolithography)
- Use: Suitable for detailed models, such as jewelry or medical applications.
- Materials: Liquid resins that cure with UV light.
- Advantages: Extremely detailed prints.
- Disadvantage: Requires more post-processing and is more expensive.
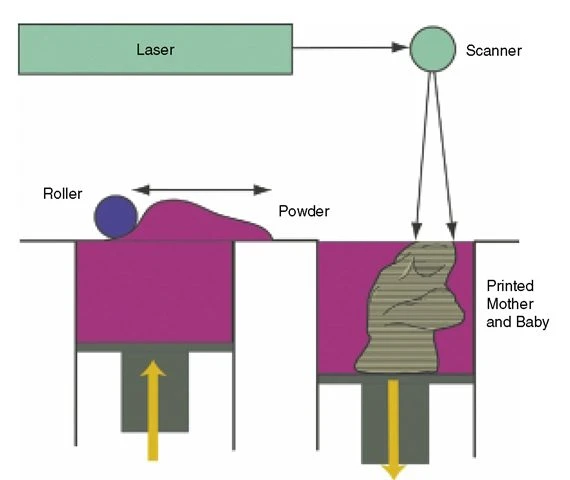
SLS printers (Selective Laser Sintering)
- Use: Industrial applications such as aerospace and automotive industries.
- Materials: Powders such as nylon and metal.
- Advantages: No support structures required, ideal for complex designs.
- Disadvantage: Very expensive, only for expensive materials
Multi-material and multi-colour printers
There are several ways to get multiple colors in 3d printing. The most common (old) technique is painting a model. This is done with a small brush and a lot of post-processing. Since the Bambu Lab printers, there is a possibility to easily print multiple colors/materials. Before, it was also possible to manually add a pause and change the filament. Bambu Lab has automated this process with the AMS (Automatic Material System). Previously, it was also possible to print multiple colors with multiple print heads. Where each color or material got its own print head. However, the calibration of this was very complicated and it never really worked properly.

3D printing materials
Choosing the right material is essential for a successful project. Here is a rundown of the most popular options:
- Advantages: Biodegradable (The material is made from corn), easy to print, ideal for beginners.
- Applications: Decorative objects, toys and prototypes.
- Polymaker PLA: A premium choice due to its consistency and high quality.
2. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- Advantages: Strong, durable and heat resistant.
- Applications: Functional parts such as housings.
- Disadvantage: Requires a heated print bed and good ventilation and is therefore very difficult to print with.
3. PETG (Polyethylene terephthalate glycol)
- Advantages: Combines strength and flexibility, resistant to moisture and heat.
- Applications: Functional parts and food safe applications.
- Our advice is that stronger models should be printed.
4. Special materials
- Metal and wood composite: For decorative and structural applications.
- Flexible filaments: For elastic parts such as seals.
Applications of 3D printing
Prototyping
- 3D printing accelerates the product development process.
- 3D printing products does not require molds or other expensive tools. A quality 3D printer can create a good product without post-processing.
- It provides an affordable way to test multiple iterations.
- The fast production method makes it easy to do a test print to test dimensions.
2. Medical sector
- Prosthetics: Customizable and affordable.
- Currently, various prostheses are printed on 3d printers. This does not require expensive injection molding machines and can easily produce a custom prosthesis.
- Surgical Devices: Custom-made instruments improve precision.
- Some surgeries require very specific instruments. Where previously these were made of surgical steel, they can now be printed with surgical plastic within a few hours.
- Bioprinting: Experimental, but promising for printing tissues.
- There are several companies developing 3D printers that can print tissue, muscle and even bone.
3. Construction and architecture
- Maquettes: Detailed scale models of buildings.
- Where previously models were handmade from cardboard or other materials, they can now easily be printed from the 3D design and assembled.
- Direct construction: Experiments with printing complete houses.
- The first fully 3D printed homes and bridges have now been completed and are being used.
4. Education
- STEM Education: Students learn to design, program, and solve problems.
- Looking to the future, we are increasingly busy teaching children/students more technical education. In this, 3D printing is a very good mix between easy to learn and fun to do for everyone.
- Art and design: Creative projects drive innovation.
- The new art is sustainable, reusable, recycled, but also special, technical and complicated. 3D printing offers more dimensions to implement in art.
Cost of 3D printing
Purchase costs of printers
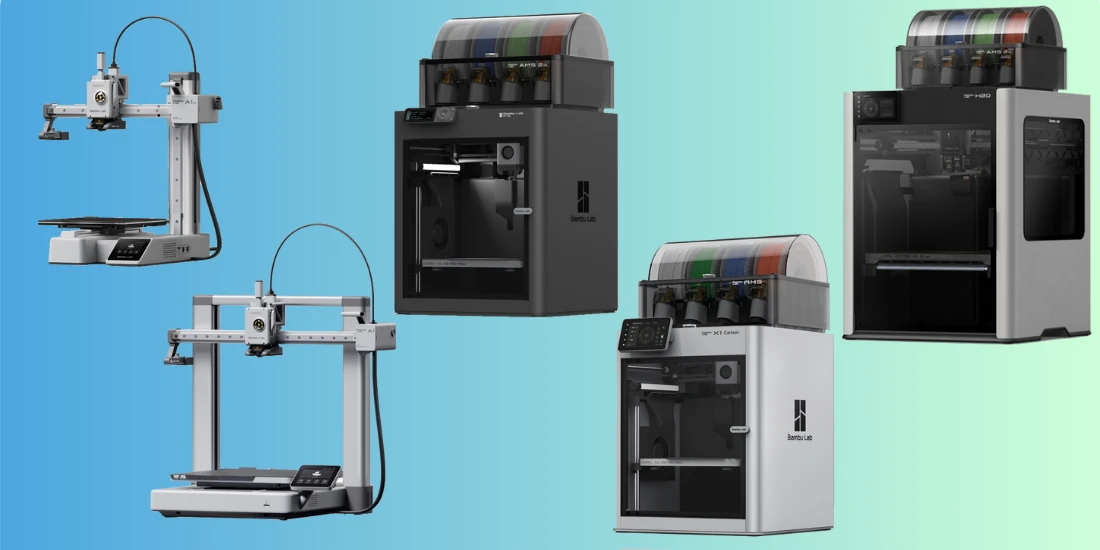
- Beginner Sprinters: From €200 - €300, such as the Bambu Lab A1 Mini .
- High-end models: The Bambu Lab X1 Carbon combo costs around €1500.
- Industrial printers : Costs start at €10,000.
- PLA filament: €20-€30 per kilo.
- Depending on the colour composition and materials.
- Special materials: Resins or metal powders are more expensive.
- up to €60 to €100 per half kilo
3. Other costs
- Software: Almost all 3D printers come with a free slicer software.
- Maintenance : Regularly clean and replace parts such as nozzles.
- Around €50 per year
How does 3D printing work?
3d printing for beginners:
- Choose a printer :
- The Bambu Lab A1 series printers are ideal for ornate models printed exclusively from PLA
- The Bambu Lab P1 series printers offer more possibilities in different materials such as PETG.
- The Bambu Lab X1 series printers are everything you need in a 3d printer, speed, quality and material choice.
- Use simple designs: Download free models from websites like Makerworld .
- Learn the basics: Understand how settings like temperature and speed work.
- Work safely: Ventilate well.
3D Printer Maintenance Tips
- Clean the nozzle regularly: This prevents clogging.
- Clean and grease the guides: This prevents the print head from slipping.
- The Bambu lab 3d printers will indicate themselves when the guides need to be cleaned, including a link to an explanation of how to do this.
- Store filaments dry: Use a storage box with silica gel.
- The AMS from bambu lab also has a passive way of drying out the filament
- not with the AMS Lite
- The AMS from bambu lab also has a passive way of drying out the filament
Innovations in 3D printing
- Multi-color printing: The Bambu Lab AMS system enables colorful creations.
- Sustainable materials: Biodegradable and recyclable filaments are becoming increasingly popular.
- New applications: 3D printing in space and medical sectors continues to grow.
Conclusion
3D printing opens the door to a world of possibilities. Whether you are a beginner looking to create simple projects or a professional creating complex designs, there is a 3D printer and a material to suit your needs. Elektronica Voor Jou offers all the products to help you get started with 3D printing.