5413+ reviews
Order by 16:00 for same day shipping
14 days return
DE
EN
Individual
Business
Raspberry Pi Pico – Lesson 4: Raspberry Pi Pico Analog Sensor Readout
In this project you will learn how to read an analog sensor with a Pico & MicroPython. This hands-on tutorial is perfect for beginners who want to get started with the Thonny programming tool and MicroPython. Learn step by step how to connect the Raspberry Pi Pico to your computer, upload programs and read an analog sensor, such as a potentiometer on the ADC of the Pico. Explore the world of analog sensors with this hands-on tutorial and take your first steps in using the Raspberry Pi Pico for sensory applications!
This manual covers:
This is the fourth lesson of the Raspberry Pi Pico introductory projects. Before starting this lesson, we recommend that you complete the previous lessons. Lesson 3 can be found HERE , lesson 1 can be found HERE .
Installing Software on the Raspberry Pi Pico for the Analog Sensor
You can skip this step if you already did this in Lesson 1.
In order to program the Raspberry Pi co with MicroPython we first need to flash the firmware of the Pico.
This means that we provide the internal software that starts the pico with a special python version.
Download firmware from the website below (uf2 file)
https://micropython.org/download/RPI_PICO/
https://micropython.org/download/RPI_PICO_W/
(Make sure you select the correct firmware version, the wifi version and the non-wifi version are different)
Press and hold the white boot button on the pico.
Plug the pico into a USB port on your computer. (Then you can release the button)
A drive letter, accessible like a memory stick, will now appear.
Copy the firmware file RPI_PICO_xxxxxx.uf2 to this drive
(pico will reboot and the firmware will be installed)
Download and install Thonny on your PC.
( https://thonny.org/ )
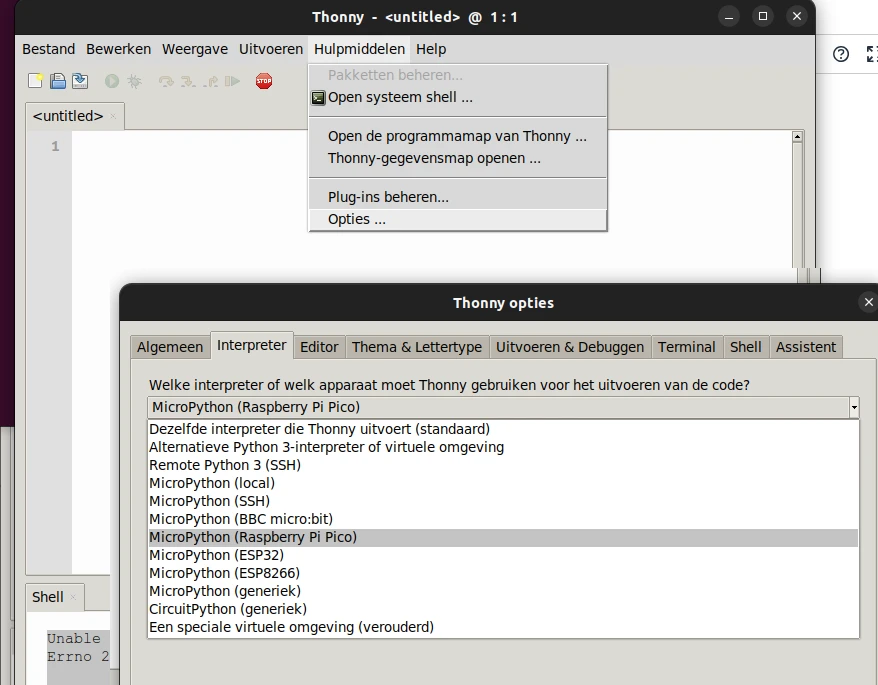
Select the MicroPython Interpreter under
Tools > Options > Interpreter > MicroPython ( Raspberry Pi Pico)
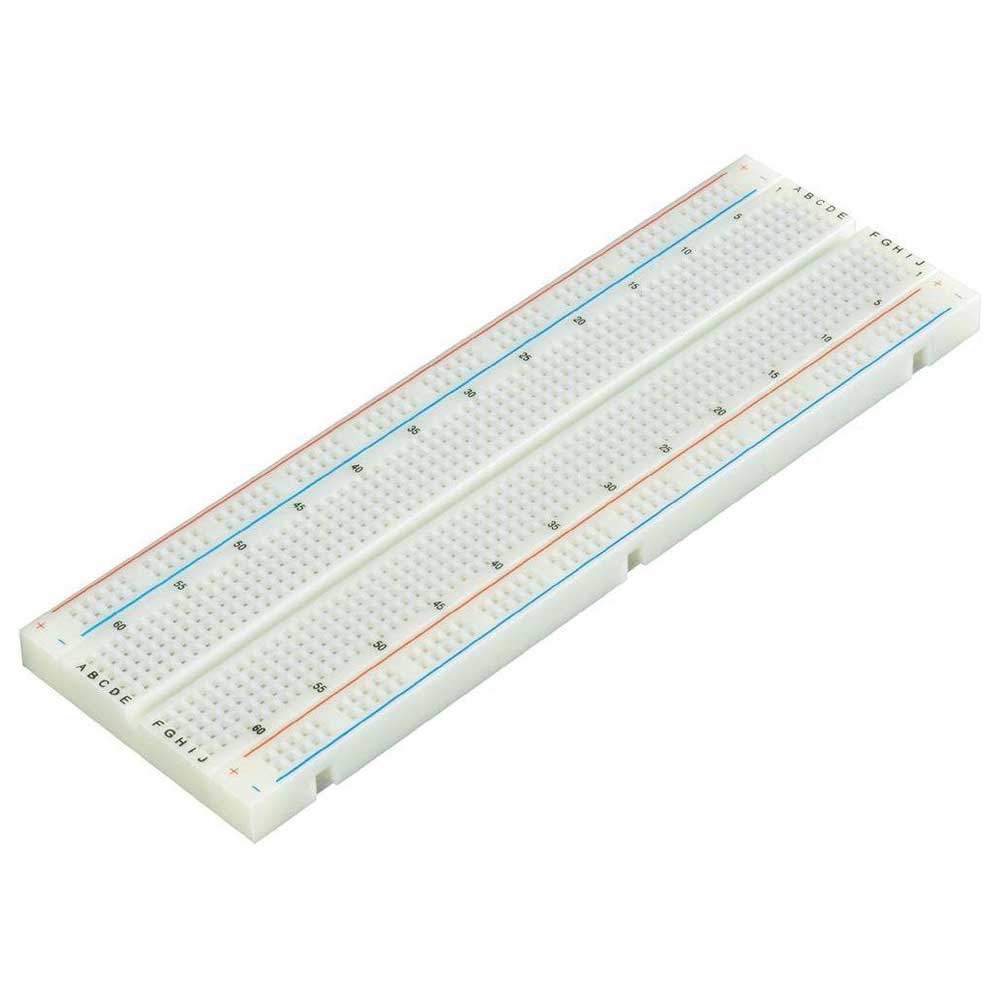
Place the components on a breadboard as shown below.
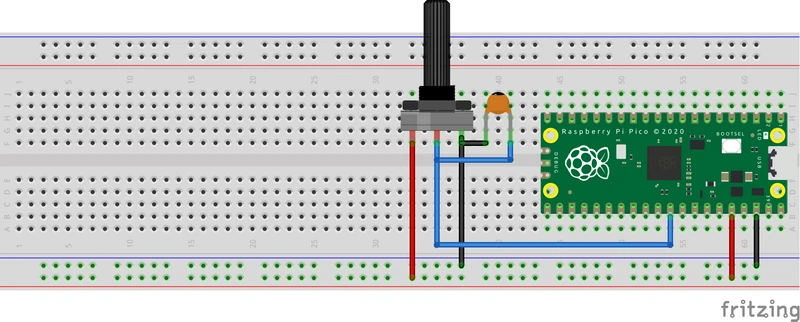
The potentiometer (adjustable resistor) is 10K ohm.
The capacitor used is 0.1uF. This will make the readings a bit more stable, but is not needed for testing.
Programming the Raspberry Pi Pico to read the potentiometer
Now you can retype the program below into the Thonny interface.
from machine import ADC
from time import sleep
analoog = ADC(26) # adc0
while True:
waarde = int(analoog.read_u16() )
# Onderstaande geeft waardes van 0 - 255
# waarde = int(analoog.read_u16() /256)
print("Analoge waarde is : " + str(waarde))
sleep(1)Explanation of the program:
- Import the ADC class (Analog digital converter) from the python machine module
- Import the sleep class from the time module
- .
- Read Pin 26 adc0
- Here an endless loop is started
- enter the read analog value from pin 26 (adc0) into the variable value
- comment on the example, the reading is accurate but will also fluctuate a lot.
The capacitor will counteract some of this interference, another solution is on line 8 - In this line, remove the # and put it in front of 7. Now the readout will show a smaller range, but the advantage is that the read values are more stable.
- Print the read value
- wait 1 second and start again
Then press save, and save the program on your own computer.
Press the red stop sign button to restart the 'backend'.
(Thonny is now reconnecting to your Pico)
Then you could press green button (Run current script).
If the pico is now removed from the computer and reconnected the program will not start.
We only tested the programming code.
To enable automatic start we need to save the program again, but then select the pico.
File > Save As > Raspberry Pi Pico
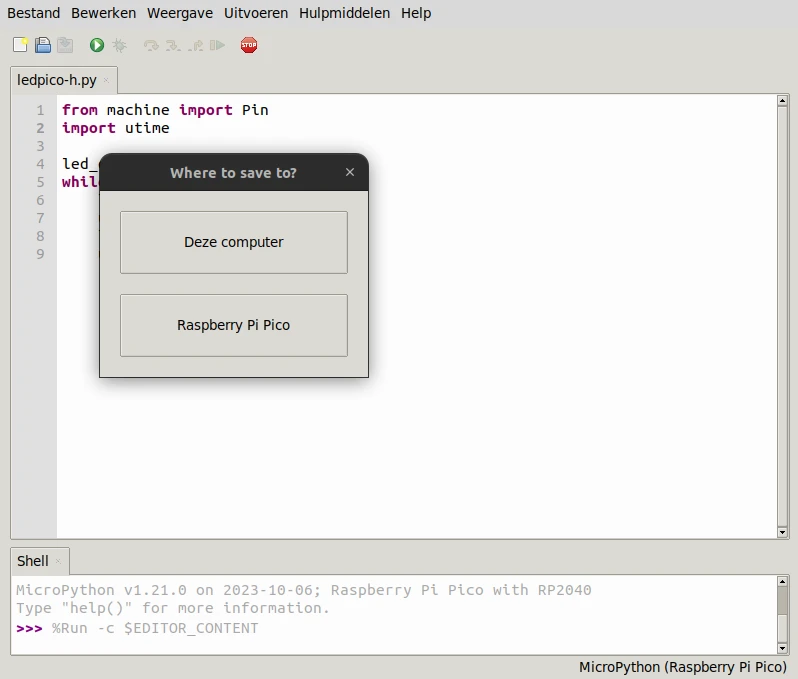
Save the program with the name main.py . The pico will automatically start the program with this name when you connect the Pico to a USB port.
In this case you will need a connection to your PC and Thonny to see the measured results!
Result: Read analog sensor with the Raspberry Pi Pico
You have now learned how to read an analog sensor yourself using a Raspberry Pi Pico.
Did you enjoy doing this project? Check out our other projects, or Lesson five of this Pico series!