5368+ reviews
Order by 16:00 for same day shipping
14 days return
DE
EN
Individual
Business
11/03/2025
All about the ESP32 & ESP8266
In the modern world, we are increasingly connected. If you want to take the next step in programming, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a great place to start. ESP chips have become incredibly popular in recent years due to their low price and the ability to connect them to the internet. The ESP32 or ESP8266 can be controlled with the Arduino IDE, making them easy to use. It is a great option for anything internet related.
What is a SOC?
The ESP8266 and 32 are SOC (system on chip). A system on chip is a more powerful microcontroller. A SOC often has a powerful processor (CPU) and a GPU. A SOC is usually built around a microcontroller or a microprocessor. SOC can be found in mobile phones, microwaves, robots, hospital equipment and cars.
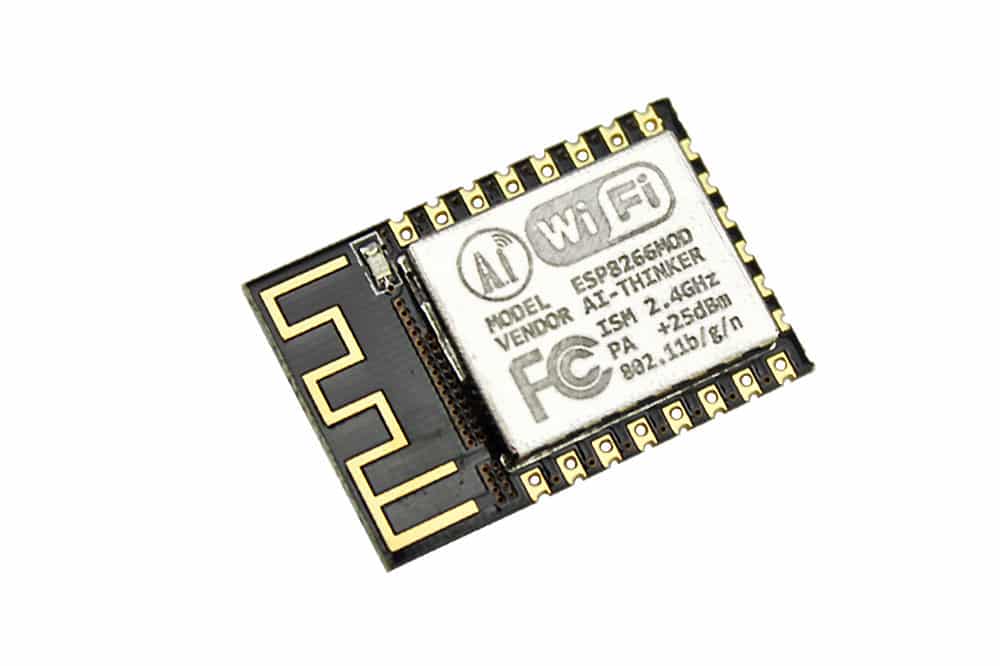
The ESP8266
The ESP8266 is a SOC specifically designed to connect to the internet.
Espressif released the ESP8266 in 2014 and it is still very popular for all IoT related projects. You can use the ESP8266 by using the AT command firmware or by connecting it to a microcontroller. By using the UART (universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter). You can also write your own firmware with an SDK.
The ESP8266 can use analog, input, output, PWM, SPI, I2C pins. This allows you to easily use the ESP together with a microcontroller.
An ESP8266 as an Arduino
You can also use the ESP8266 as a microcontroller (for this it is smart to use a module with an ESP). This is a popular choice because the ESP8266 is cheaper than an Arduino and it can connect to the internet.
The ESP8266 has enough pins for components like LEDs, servos, lcd screens, etc. It is important to know that some pins can not handle 5 volts and therefore only output 3.3. The ESP8266 has 17 pins that seems enough but due to an error you can not use pins GPIO6 to GPIO11. You can also not use the GPIO1 for LEDs otherwise the ESP will crash. (source)
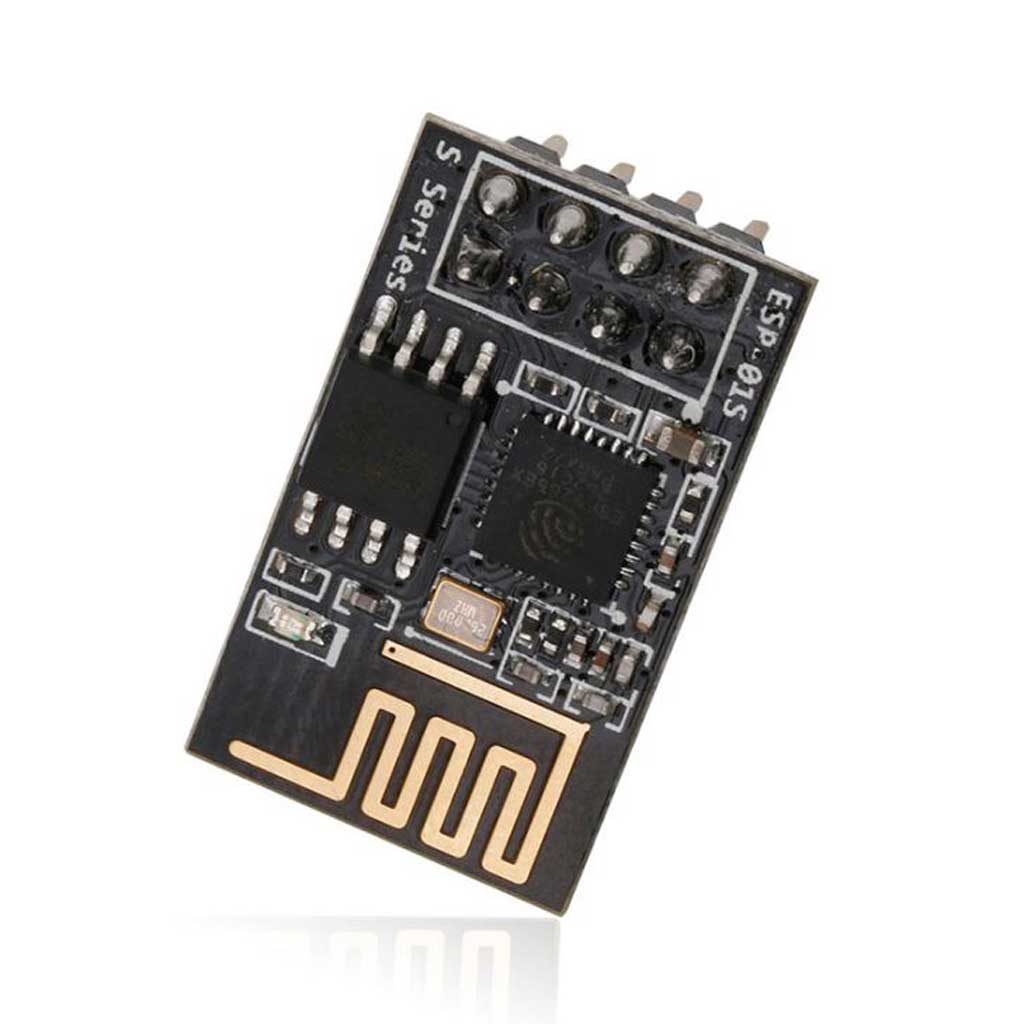
ESP-01 module
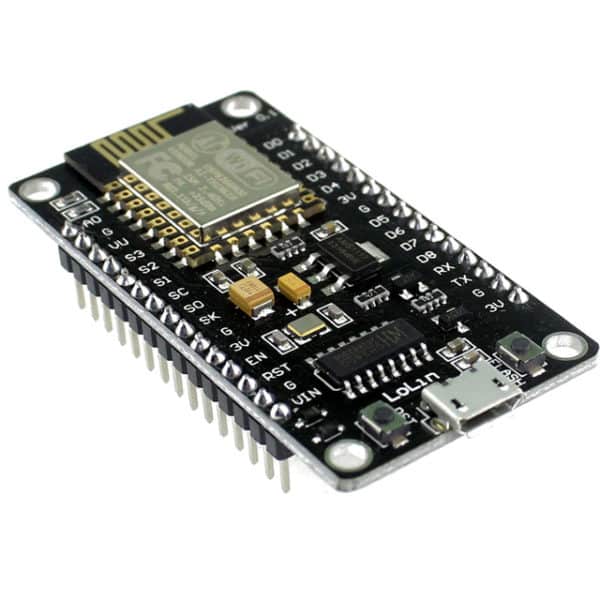
NodeMCU DEVKIT 1.0
The NODEMCU ESP8266 Development board is also widely used to control the ESP8266. You program this board with LUA script. LUA is a programming language just like C+ and Python. LUA is often used for video games. NodeMCU also has an open-source software to use this board. This is an easy alternative for those who do not want to use an Arduino.
SDK
To use an ESP8266 you need to be able to control it. This can be done with an SDK (software development kit). In 2014 Espressif released their own SDK to program the chip without a microcontroller. However, there are many other ways to use the ESP8266. A popular way is the Arduino.
To use the ESP8266 with an Arduino, all you need to do is download the appropriate library and connect the ESP.
Furthermore, you can program the ESP8266 in languages such as Python, Lua or JavaScript.
SDK for the ESP32
Of course, there are also several choices when it comes to programming for the ESP32.
For example, you can use the Arduino library for the ESP32 in the same way you would program the ESP8266.
Just like for the ESP8266, you can also use NodeMCU for the ESP32.
The ESP-IDF (ESP IoT Development Framework) is the official software from Espressif and specifically designed for use with the ESP32.
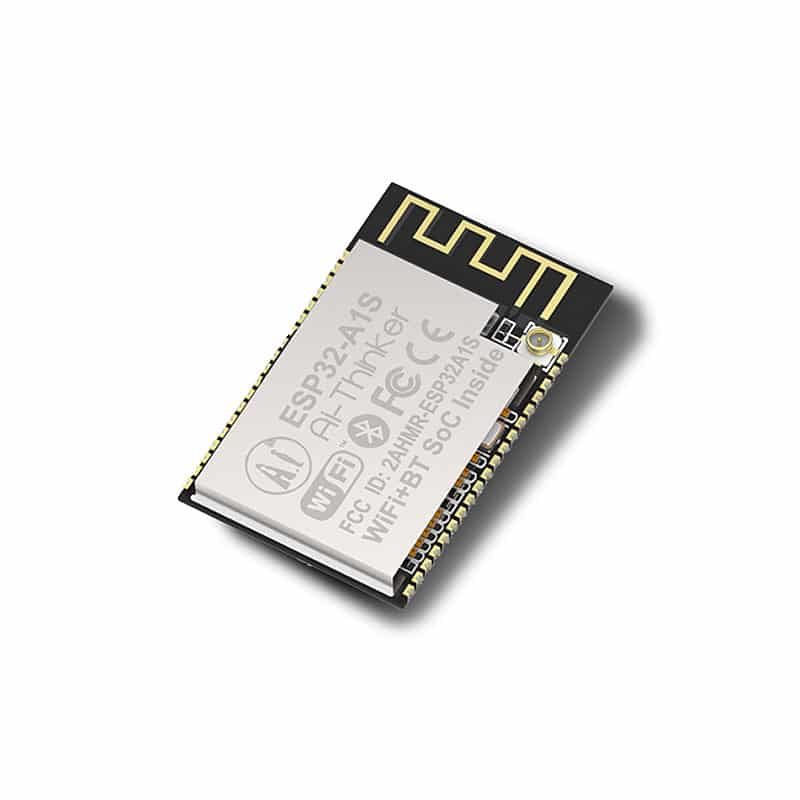
ESP32
After the success of the ESP8266 came the ESP32 it can do everything the ESP8266 can but is only much more powerful. The ESP32 is also used in the NINA-W10. This module is used in almost all Arduino boards that can connect to the internet. The ESP32 can also use bluetooth a function its predecessor did not have.
All these extra features make the ESP32 sometimes twice as expensive as the ESP8266.
The ESP32 is better than the ESP8266 in many ways, but especially in the extra built-in features.
Features of the ESP32
To start with, the ESP32 has 34 pins, which is double the ESP8266 with only 17 pins.
CAN (Controller Area Network)
This is a feature that only the ESP32 has. This feature ensures that electromagnetic interference does not have such a big influence on the signal transmission.
Touch sensor
The ESP32 has 10 capacitive Touch GPIO pins. This means that they can pick up small variations in electricity, like human skin.
Temperature Sensor
This allows the ESP32 to measure the temperature. Only because everything in the chip is very close together, this value can be inaccurate due to the heat of the rest of the chip.
Hall effect sensor
With this sensor, the ESP32 can measure changes in the magnetic field. This can be used to detect if something is moving nearby, to observe the rotations on a wheel, and much more.
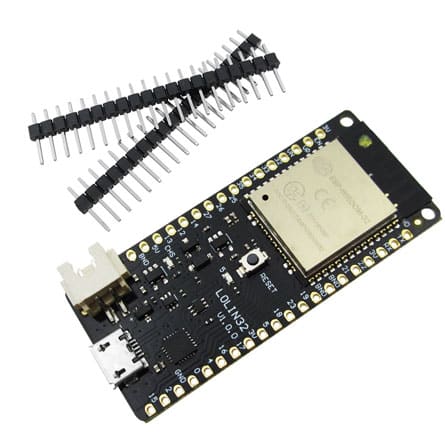
ESP32 devkit doit
A commonly used board for the ESP32 is the ESP32 Development board .
This board has 30 to 36 pins and has Lua script support through the NodeMCU software. You can also use it in the Arduino IDE through the USB-to-UART connection.
Specifications ESP32 and ESP8266
The best way to decide between the ESP32 and the ESP8266 is to compare their specifications.
| Specifications | ESP32 | ESP8266 |
| MCU (microcontroller unit) | Xtensa Dual-Core 32-bit LX6 with 600 DMIPS | Xtensa Single core 32 bit L106 |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 4.2 and BLE | X |
| SRAM | ✓ | X |
| FLASH | ✓ | X |
| GPIO | 34 | 17 |
| Software PWM | 16 | 8 |
| SPI/I2C/I2S/UART | 4/2/2/2 | 2/1/2/2 |
| ADC | 12-bit | 10-bit |
| CAN | ✓ | X |
| Ethernet MAC Interface | ✓ | X |
| Touch Sensor | ✓ | X |
| Temperature Sensor | ✓ | X |
| Hall effect sensor | ✓ | X |
| Min/max temperature | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC |
What is the best choice?
If you compare the ESP32 and ESP8266, the choice seems easy. However, the ESP8266 can be useful for cheap projects or tests. A big advantage of the ESP8266 is that it has been around for a longer period of time, so there is more information available about it. This is very useful, for example, for an error message that you do not know. If someone else has already solved it, you do not have to do it anymore. There are also better libraries for the ESP8266. However, the ESP32 will eventually receive just as much documentation and information.
Getting started with ESP?
We found the use of the ESP8266 and ESP32 very easy. After installing the right boards it was as easy as programming an Arduino. I mainly used the ESP32 DEVKIT DOIT. This module was difficult to set up but once that was done the programming was very easy. I had a lot of fun with the ESP32. If you want to start a project that uses the internet the ESP32 is definitely recommended.