5368+ reviews
Order by 16:00 for same day shipping
14 days return
DE
EN
Individual
Business

28/07/2025
3D Printing Filaments – Everything You Need to Know!
3D printing filament is the material used to print with an FDM printer. An FDM printer builds its models layer by layer by means of additive printing. The filament is a plastic thread that is heated until it spins. The filament is then placed in the right place and cooled again until it solidifies. In this way, fdm printers work accurately and with as little waste as possible. Filament comes in many different types, colors, weights and even sizes.
Why is choosing the right filament important?
Choosing the right filament is crucial. This material forms the basis of every 3D printed model. The print head melts it and places it precisely. Not every printer works with every filament. Materials differ in printing requirements such as temperature and humidity. If you use the wrong filament, you run the risk of clogging the print head or even a fire hazard.
But it's not just about the type of material. Quality plays a big role. Reliable brands guarantee a constant diameter. This prevents problems such as under- or over-extrusion. Irregular thickness can lead to failed prints or dangerous situations.
Cheap filament, especially from platforms like AliExpress, sometimes contains impurities. For example, PLA (PolyLactic Acid) must be made entirely from corn derivatives. Budget versions sometimes contain other plastics. This can clog nozzles or even pose a fire hazard.
In addition, moisture absorption is a point of attention. Some filaments quickly attract moisture. This affects the print quality and can cause brittleness or air bubbles. That is why storage is just as important as the choice of filament itself. Store rolls dry or use a drying box.
Temperature is also a crucial factor. Each filament has a specific printing temperature. Is the temperature too low? The material will not adhere properly. Is it too high? The nozzle can clog. Manufacturers provide guidelines, but minor adjustments may be necessary for the best result.
So choose filament that is safe, reliable and easy to print. On our site you will only find carefully tested options. We fully support their quality. This way we guarantee a smooth printing experience and the best end result.
The Basics of 3D Printing Filaments
What is filament and how is it made?
Filament is the material that a 3D printer uses to build objects. It consists of a thin thread of thermoplastic plastic, rolled up on a spool. The printer melts this and lays it down layer by layer to form a model.
How is filament made?
The process starts with plastic granules (granulate). These are heated to a thick liquid. Then a machine presses it through a narrow opening. This creates a thin wire. This wire is cooled, measured and rolled up.
Some filaments contain additives such as wood fibers, metal particles or carbon fiber . This changes the appearance and strength of the material.
How does filament work in a 3D printer?
A 3D printer pulls the filament through an extruder . There it is heated to 180-250°C , depending on the type. The molten plastic comes through a nozzle and is placed on the print bed . This is done layer by layer. The process is called Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) .
To print well, a few things have to be right:
- Temperature: Too hot produces drips, too cold clogs the nozzle.
- Speed: Slow gives better details. Too fast causes errors.
- Adhesion: A heated print bed prevents warping.
- Cooling: Some filaments need to cure quickly.
Filament comes in many types, such as PLA, ABS and PETG . Each has unique properties. There are also flexible or glossy varieties.
Filament allows hobbyists, engineers and designers to create objects quickly and affordably.
Different diameters: 1.75 mm vs. 2.85 mm
When choosing filament for your 3D printer, the diameter is one of the most important specifications to consider. The wrong diameter can lead to bad prints or even blockages in your printer.
The Two Standard Diameters
In general, there are two standard filament diameters used in the 3D printing industry:
- 1.75mm filament
- 2.85mm filament (sometimes rounded to 3.00mm)
Both formats have their own pros and cons, depending on your printer and application.
1.75mm Filament
1.75mm filament is the most common diameter nowadays and is supported by most desktop 3D printers. Some advantages of 1.75mm filament:
- Better precision : Because the filament is thinner, the extruder can push it through the nozzle more precisely and with less resistance.
- Faster Heating : Thinner filament heats up faster in the hotend, resulting in a more efficient melting process.
- Wider Compatibility : Most modern 3D printers, including popular brands like Bambu Lab, use standard 1.75mm filament.
One minor drawback is that 1.75mm filament can be more susceptible to kinking and breaking, especially with flexible materials like TPU.
2.85mm Filament
Although 2.85mm filament is less common than 1.75mm, it still has a loyal user base, especially among Ultimaker users. The advantages are:
- Stronger Extrusion : Because the filament is thicker, the extruder can extrude more powerfully and with less slippage, which is beneficial for larger prints.
- Less prone to kinking : The stiffer nature of thicker filament makes it less prone to bending in the Bowden tube.
- Suitable for large nozzles : Printers designed for industrial applications or large prints may work better with 2.85mm filament.
One disadvantage of 2.85mm filament is that it is less common, which can limit the choice of filament types and colors.
Which Diameter Should You Choose?
The choice between 1.75mm and 2.85mm filament depends on your printer. It is important to check the specifications of your 3D printer before purchasing filament. In general:
- Use 1.75mm if you have a modern desktop 3D printer and are looking for versatility.
- Use 2.85mm if you have a printer specifically designed for this size, such as some Ultimaker models.
The Most Popular Types of 3D Printing Filaments
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA ( Polylactic Acid) is a popular material for 3D printing . This bioplastic comes from renewable sources such as cornstarch and sugar cane. It is more environmentally friendly than petroleum-based plastics. PLA is easy to print due to its low melting temperature (180-220°C) and has a low odor. This makes it ideal for both beginners and experienced makers.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- Easy to print – Low shrinkage and adheres well to the print bed, minimizing warping.
- More environmentally friendly – Made from renewable resources and biodegradable in industrial composting conditions.
- Many variants – Available in various colours and finishes, such as transparent, wood and metal filled.
- Low Odor and Safe – Produces virtually no harmful fumes and is suitable for home and school use.
Disadvantages
- Low heat resistance – Softens at 50-60°C, making it less useful in hot environments.
- More brittle than ABS – Less flexible and impact resistant, making it more likely to break.
- Limited outdoor applications – Sensitive to heat and UV light, causing it to degrade faster outdoors.
Applications
PLA is widely used in 3D printing projects including:
- Prototyping and model making – Ideal for concept models and visual prototypes due to easy printability.
- Decorative objects – Suitable for figurines, jewelry and works of art thanks to the variety of colors and finishes.
- Education – Popular in schools and universities due to its low toxicity and simple settings.
- Functional, lightweight parts – For example, housings, cable holders and mechanical components without heavy loads.
Despite some limitations, PLA remains an excellent choice for most 3D printing applications. It is especially suitable when heat resistance and mechanical strength are not a priority.
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene)
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its strength and heat resistance. This material is not only used in 3D printing, but also in the production of consumer goods such as LEGO bricks, household appliances and automotive parts. ABS has a higher printing temperature (around 220-250°C) and is more resistant to mechanical stress than PLA, but is also more challenging to print due to shrinkage and warping.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- Strong and impact resistant – ABS is much tougher than PLA, making it suitable for mechanical parts and functional prints.
- High heat resistance – Can withstand temperatures up to approximately 100°C without deformation, ideal for applications with heat exposure.
- Machinable – ABS can be sanded, drilled and glued, and the surface can be finished with acetone for a smooth, glossy look.
- Durable – Resistant to chemical influences and has a longer lifespan than PLA, especially in functional applications.
Disadvantages
- More difficult to print – ABS tends to warp and requires a heated print bed (90-110°C) and preferably an enclosed print chamber.
- Strong odor and fumes – Printing produces fumes that may be irritating; a well-ventilated area is necessary.
- Less environmentally friendly – Unlike PLA, ABS is not biodegradable and is made from fossil fuels.
When do you choose ABS?
ABS is the right choice when you need a material that is strong and heat resistant. Choose ABS in the following situations:
- Functional and mechanical parts – For example, gears, housings, tools and structural components.
- Outdoor and industrial applications – ABS is more resistant to higher temperatures and chemical influences than PLA.
- Parts requiring post-processing – The ability to sand, paint, and release acetone fumes makes ABS ideal for applications where a smooth finish is desired.
- Prototype development for mass production – Since ABS is widely used in injection molding, 3D printed ABS prototypes can be easily converted to mass production.
Although ABS is more difficult to print than PLA, it offers significant advantages for users who need functional, heat-resistant, and durable prints.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is a versatile 3D printing material that combines the strength and heat resistance of ABS with the ease of printing of PLA. It is a modified version of PET (known from plastic bottles), in which the addition of glycol (G) ensures less brittleness and better processability. PETG is popular because of its high toughness, chemical resistance and moisture resistance, making it suitable for functional and outdoor applications.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- Strong and flexible – PETG is tougher than PLA and less brittle than ABS, allowing it to withstand mechanical stress without breaking easily.
- High heat resistance – More heat resistant than PLA (up to about 80°C), but easier to print than ABS.
- Moisture and chemical resistant – PETG has low moisture absorption and is resistant to many chemicals, making it suitable for functional applications.
- Easy to print – Adheres well to the print bed and suffers less from warping than ABS. A heated bed (around 70-90°C) is recommended for best results.
- Recyclable – PETG is recyclable and more sustainable than ABS, although it is not biodegradable like PLA.
Disadvantages
- Less stiff than PLA – PETG is more flexible, but that can also be a disadvantage in applications that require rigid structures.
- Risk of stringing and blobs – PETG is prone to oozing, making it necessary to tune retraction settings carefully.
- Less easy to machine – Unlike ABS, PETG cannot be smoothed with acetone and is more difficult to sand.
Best Applications
PETG is ideal for a wide range of applications where both strength and durability are required:
- Functional parts – Such as gears, holders, and parts that must withstand mechanical stress.
- Outdoor and water resistant applications – PETG is resistant to moisture, UV rays and chemicals, making it suitable for outdoor use.
- Food-safe applications – Some PETG variants are food-safe, making them suitable for use in bottles and kitchenware, for example (pay attention to certification).
- Transparent and translucent prints – PETG is available in bright colors and can be used for lampshades or other transparent applications.
- Medical and Industrial Applications – PETG is used in the medical sector due to its chemical resistance and sterilizability.
PETG offers an excellent balance of strength, flexibility and ease of printing, making it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals who need functional and durable prints.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) - Flexible filament
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a flexible 3D printing material known for its elasticity, shock resistance, and abrasion resistance. Unlike PLA, ABS, and PETG, which are relatively stiff, TPU can bend and rebound without breaking. This makes it an excellent choice for applications that require flexibility and durability. TPU has a printing temperature of around 210-250°C and adheres well to the print bed without much warping.
When do you use TPU?
TPU is ideal for applications where elasticity and wear resistance are important:
- Wear-resistant and impact-resistant parts – Think of protective covers, shock absorbers and wheel tires.
- Flexible joints and seals – Ideal for gaskets, seals and hinges that are subject to regular loads.
- Wearables & Accessories – TPU is soft and skin-friendly, making it suitable for watch straps, phone cases, and wearable technology.
- Robotics and engineering – Used for flexible couplings, gripping mechanisms and moving parts in machines.
- Medical applications – Due to its biocompatibility and chemical resistance, TPU is also used for prosthetics and orthopedic devices.
Tips for successful printing
Printing TPU is more challenging than PLA or PETG due to the flexibility of the filament. Here are some important tips for a successful print:
- Use a direct-drive extruder
- TPU works best with a direct-drive extruder, as a Bowden extruder can have difficulty feeding the flexible filament smoothly.
- Reduce the print speed
- Print slowly, ideally around 15-30mm/s , to avoid clogs and inconsistencies.
- Optimize the retraction settings
- Use a low retraction speed and distance to minimize clogging and oozing (filament drips).
- Make sure the print bed is clean and warm
- A heated print bed at 40-60°C with a clean and well-bonded substrate (such as PEI, glass or a glue stick) will prevent delamination.
- Limit the extrusion pressure
- Because TPU is flexible, too much pressure in the extruder can cause the filament to deform and jam. Lower extrusion pressure helps prevent this.
- Use minimal or no fan
- TPU has good interlayer adhesion and usually does not require cooling unless the print contains fine details.
- Store TPU dry
- TPU is hygroscopic and absorbs moisture quickly, which affects the print quality. Store it in an airtight container with silica gel.
With the right settings and considerations, TPU is a powerful material for applications requiring flexibility and durability.
Nylon - Strong and durable
Nylon is a robust and versatile 3D printing material known for its high strength, durability and wear resistance. This industrial filament is excellent for mechanical and functional parts that need to withstand heavy loads. Nylon has a high toughness and is flexible to a certain extent, making it less likely to break than stiffer materials such as PLA or ABS. The material is widely used in engineering and manufacturing due to its excellent mechanical properties.
Benefits and applications
Advantages
- Extremely strong and wear resistant – Ideal for mechanical and industrial applications.
- Good impact resistance – Does not break easily under load and is more resistant to shock than PLA and ABS.
- High temperature resistance – Can withstand temperatures up to approximately 100°C without deformation.
- Slightly flexible and resilient – Unlike ABS and PLA, Nylon can bend slightly without breaking, making it ideal for moving parts.
- Chemical resistant – Resistant to oils, solvents and other chemicals.
Disadvantages
- Mechanical parts – Gears, hinges, bearings and bushings that must withstand high loads.
- Industrial and automotive applications – Enclosures, functional prototypes and machine parts.
- Wear-resistant tools – Clamps, brackets and fasteners.
- Flexible and sturdy objects – Cable ties, zippers and protective caps.
Print settings and challenges
Print settings
- Extrusion temperature: 240-270°C (depending on the type of Nylon).
- Print bed system: Heated bed at 70-100°C, preferably with a PEI sheet or PVA glue for better adhesion.
- Print speed: 30-60mm/s for consistent extrusion and good adhesion.
- Store dry: Nylon is extremely hygroscopic and absorbs moisture quickly, which greatly affects print quality. Store in an airtight container with silica gel and dry before use (e.g. in a filament dryer at 70°C for several hours).
Challenges
- Poor Bed Adhesion and Warping – Nylon tends to warp during printing. A heated print bed with a strong adhesion layer (such as glue stick or Magigoo PA) will help minimize warping.
- Moisture absorption – Nylon quickly absorbs moisture from the air, which results in poor print quality (bubbles, inconsistent layers). Keeping the filament dry is crucial.
- More difficult to print than PLA and PETG – Due to high printing temperatures and sensitivity to moisture, Nylon requires a well-tuned printer and some experience to achieve consistent results.
With the right settings and preparation, Nylon is a powerful material for functional, wear-resistant and durable prints, especially in technical and industrial applications.
Special filaments
In addition to standard materials such as PLA, ABS, PETG and Nylon, there are also special filaments that offer unique properties and visual effects. These include wood-filled, metal-filled, carbon fiber reinforced and glow-in-the-dark filaments. These materials combine the base of a standard polymer (such as PLA or PETG) with special additives that improve the appearance, strength or functionality.
Wood filled, metal filled, carbon fiber, and glow-in-the-dark
Wood filled filament
Composition: PLA or PETG mixed with wood fibers.
Features:
- Gives prints a wood-like look and texture.
- Can be sanded and stained for a more realistic wood effect.
- Often a slight smell of wood during printing.
When interesting?
- For decorative prints such as figurines, works of art and scale models.
- For makers looking for a natural-looking material for interior applications.
Challenges:
- Nozzle wear due to wood particles; preferably use a hardened steel nozzle.
- May clog faster than standard PLA.
Metal filled filament
Composition: PLA, ABS or PETG mixed with metal powder (such as copper, bronze or aluminum).
Features:
- Gives a heavy, metallic appearance and can be polished.
- Not magnetic, but some varieties conduct heat better than standard filaments.
When interesting?
- For jewelry, figurines and art objects with a metallic look.
- For functional parts where extra weight is desired.
Challenges:
- Very abrasive for standard brass nozzles; a hardened or rubidium nozzle is recommended.
- Has a higher density, which can cause extra stress on the extruder.
Carbon fiber reinforced filament
Composition: Nylon, PETG or PLA with added carbon fibers.
Features:
- Extremely strong and stiff, ideal for structural applications.
- Lighter than solid metal components, yet very strong.
When interesting?
- For technical applications such as drones, robotic arms and machine parts.
- When extra strength is needed without the weight of metal.
Challenges:
- Very abrasive for standard nozzles; a hardened nozzle is necessary.
- May be more brittle than base filament depending on mix ratio.
Glow-in-the-dark filament
Composition: PLA or PETG mixed with phosphorescent particles.
Features:
- Emits light when exposed to a light source.
- Available in different colours, usually green or blue.
When interesting?
- For decorative prints such as lampshades, toys and art objects.
- For safety and warning markings in dark environments.
Challenges:
- The phosphorescent particles can wear down the nozzle faster; a hardened nozzle is recommended.
- Needs a stronger light source for a long lasting glow effect.
Conclusion
Specialty filaments offer unique possibilities for 3D printing, from aesthetic improvements to increased strength and functionality. They are of interest to makers, artists, and engineers who want to incorporate specific visual or mechanical properties into their prints. However, it is important to consider print settings and hardware (such as using a hardened nozzle) to achieve the best results.
What should you pay attention to when choosing a filament?
When choosing a filament, several factors play a role that directly influence the print quality, durability and usability of your 3D prints. The most important points of attention are explained below:
Printer Specifications and Compatibility
- Temperature Range: Check if your printer can reach the required extrusion temperatures for the filament. Some filaments, like Nylon or ABS, require higher temperatures than PLA for example.
- Extruder and Nozzle Type: Some filaments (such as flexible materials) perform better with a direct-drive extruder rather than a Bowden extruder. Additionally, abrasive materials (e.g. carbon fiber reinforced filaments) may require a hardened nozzle.
- Filament Diameter: Make sure the diameter of the filament (usually 1.75mm or 2.85mm) matches the specifications of your printer.
- Adhesion and Bed Temperature: Filaments differ in their adhesion properties; a heated print bed or a specific bed coating may be necessary for a good first layer.
Mechanical properties
- Strength and durability: Depending on the application, you need filaments with specific strength properties. For functional parts, a material with high tensile and impact strength is desired, while decorative prints often have lower requirements.
- Flexibility vs. Stiffness: Some projects require flexible materials (such as TPU for flexible housings), while other applications require stiffness and structural integrity (such as carbon fiber reinforced filaments).
- Temperature Resistance: If your printed parts need to function in hot or cold environments, choose a material that can withstand temperature fluctuations well.
Ambient temperature and storage
- Moisture sensitivity: Filaments such as Nylon and TPU are hygroscopic and absorb moisture quickly, which can lead to poor printing results. It is crucial to store these filaments in a dry, airtight container with silica gel for example.
- Storage conditions: Ensure a stable ambient temperature during storage. Extreme temperatures can negatively affect filament quality, which can lead to problems during printing.
- Print Environment: Consider where and how your printed objects will be used. Is it an indoor or outdoor application? Do your prints need to withstand UV radiation, moisture, or temperature fluctuations? Choose a filament that is suited to this.
By considering all of these factors, you can choose the right filament that fits both your printer and the specific needs of your project. This will ensure optimal print results and durable, functional objects.
Print settings per filament type
Polymaker Polyflex TPU95A
- Nozzle temperature: 210–230 °C
- Bed temperature: 25–60 °C (heated bed recommended for better adhesion)
- Print speed: 20–40 mm/s (slower due to flexibility)
- Cooling ventilation: Limited (30–50% after first layers)
- Additional tips: Preferably use a direct-drive extruder and reduce retraction to avoid filament clicks.
Polymaker Polyterra PLA
- Nozzle temperature: 190–230 °C
- Bed temperature: 25–60 °C
- Print speed: 30–70 mm/s
- Cooling: 100% fan after the first layers for optimal detail rendering
- Extra tips: Ideal for a matte finish and consistent prints with a natural look.
Polymaker Polysonic PLA
- Nozzle temperature: 210–230 °C
- Bed temperature: 30–60 °C
- Print speed: 100–300 mm/s
- Cooling: Complete cooling after initial layers
- Extra tips: Ensure good air circulation; suitable for high details and sharp prints.
Poloymaker Polylite ASA
- Nozzle temperature: 240–260 °C
- Bed temperature: 75–95 °C
- Print speed: 30–50 mm/s
- Cooling: Limited use of ventilation (maximum 20%)
- Additional tips: Use a closed print chamber for optimal UV and weather resistance and to prevent warping.
Polymaker Polylite ABS
- Nozzle temperature: 245–265 °C
- Bed temperature: 90–100 °C
- Print speed: 30–50 mm/s
- Cooling: As little as possible (or no extra cooling at all)
- Additional tips: A ventilated area and a heated, well-adhesive print bed (with glue or special coatings) are recommended.
Polymaker Polylite PLA
- Nozzle temperature: 190-230 °C
- Bed temperature: 25–60 °C
- Print speed: 50–60 mm/s
- Cooling: 100% ventilation after the first layers
- Extra tips: An easy-to-use filament that is excellent for detailed prints.
Polymaker Polylite PETG
- Nozzle temperature: 230–240 °C
- Bed temperature: 70–80 °C
- Print speed: 30–50 mm/s
- Cooling: Moderate cooling (0–20%)
- Additional tips: Ensure good bed adhesion (possibly with a glue stick or PEI layer) and watch out for stringing at high speeds.
Polymaker Polymide PA6-cf (Nylon with carbon fiber)
- Nozzle temperature: 280–300 °C
- Bed temperature: 25–50 °C
- Print speed: 30–60 mm/s
- Cooling: Little to no additional cooling
- Additional tips: Use a hardened steel nozzle, a heated and preferably closed printer and make sure the filament is properly dried.
Polymaker Polylite PC (Polycarbonate)
- Nozzle temperature: 250–270 °C
- Bed temperature: 90–105 °C
- Print speed: 30–50 mm/s
- Cooling: Limited (max 20% fan speed)
- Additional tips: A closed environment helps prevent warping; PC typically requires high extrusion temperatures and good adhesion.
Polymaker Polylite PLA+ (pro)
- Nozzle temperature: 190–220 °C
- Bed temperature: 30–60 °C
- Print speed: 30–70 mm/s
- Cooling: 100% ventilation after initial layers
- Additional tips: An improved variant of PLA with higher impact resistance and slightly better mechanical properties.
Polymaker Polylite LW-PLA (Lightweight PLA)
- Nozzle temperature: 190–210 °C
- Bed temperature: 25–60 °C
- Print speed: 30–50 mm/s
- Cooling: 100% ventilation
- Additional Tips: Designed for lightweight prints; maintain a consistent filament supply for optimal results.
Polymaker Polymax PETG-ESD
- Nozzle temperature: 250–290 °C
- Bed temperature: 70–80 °C
- Print speed: 30–50 mm/s
- Cooling: Moderate cooling (0–20%)
- Additional tips: Specially developed for applications where electrostatic discharge (ESD) plays a role; ensure stable extrusion.
Polymaker PolyMax PLA
- Nozzle temperature: 190–230 °C
- Bed temperature: 25–60 °C
- Print speed: 40–60 mm/s
- Cooling: 100% after the first layers
- Extra tips: Combines the ease of printing of PLA with improved strength; ideal for functional prototyping.
Bambu Lab ABS
- Nozzle temperature: 240–280 °C
- Bed temperature: 90–100 °C
- Print speed: >300 mm/s
- Cooling: As little as possible (0-80%)
- Additional tips: Take advantage of a closed printing environment for consistent print quality.
Bambu Lab PETG
- Nozzle temperature: 230–260 °C
- Bed temperature: 60–80 °C
- Print speed: <300mm/s
- Cooling: Moderate cooling (0–80%)
- Additional tips: Optimize adhesion with a well-prepared print bed and, if necessary, additional adhesives.
Bambu Lab PAHT-CF (High Temperature PA with Carbon Fiber)
- Nozzle temperature: 230–300 °C
- Bed temperature: 100–120 °C
- Print speed: < 100 mm/s
- Cooling: As minimal as possible (0-40%)
- Additional tips: Requires a hardened nozzle, a closed print environment and a dry filament due to the carbon fiber reinforcement.
Bambu Lab PA6-CF (PA6 with carbon fiber)
- Nozzle temperature: 260–300 °C
- Bed temperature: 90–120 °C
- Print speed: < 100 mm/s
- Cooling: Low (0-40%)
- Additional tips: Ensure good drying technique and use a hardened nozzle to reduce wear on the fibres.
Bambu Lab ASA
- Nozzle temperature: 240–280 °C
- Bed temperature: 90–100 °C
- Print speed: < 300 mm/s
- Cooling: Very limited (0-80%)
- Additional tips: A closed print chamber is recommended to prevent color fading and warping.
Bambu Lab PLA Basic
- Nozzle temperature: 190–230 °C
- Bed temperature: 55–65 °C
- Print speed: < 300 mm/s
- Cooling: 50-100% after the first layers
- Extra tips: A reliable filament with standard PLA properties; ideal for everyday use.
Bambu Lab TPU 95A HF
- Nozzle temperature: 220–240 °C
- Bed temperature: 30–35 °C
- Print speed: < 200 mm/s
- Cooling: Limited (50–100%)
- Additional tips: Due to the high flexibility, a direct-drive extruder is recommended; minimize retraction to prevent blockages.
Bambu Lab PLA Aero
- Nozzle temperature: 220–260 °C
- Bed temperature: 35–45 °C
- Print speed: < 180 mm/s
- Cooling: 100% after initial layers
Additional Tips: Specially developed for a smooth, sleek finish and lightweight prints, ideal for aerodynamic applications.
Problems and Solutions for 3D Printing with Filament
Warping
Problem:
Warping occurs when the bottom of a print does not adhere properly to the print bed and therefore pulls up, resulting in warping or even loose prints.
Solutions:
- Heated print bed: Ensure a stable and suitable bed temperature (e.g. 50–60 °C for PLA, 90–110 °C for ABS/ASA).
- Improve bonding: Use adhesive, PEI or BuildTak surfaces to enhance bonding.
- Print Room: Work in a closed or heated environment to minimize temperature fluctuations.
- Optimize first layer: Reduce print speed for the first layer and increase extrusion for a solid base.
Stringing (Threads)
Problem:
Stringing occurs when unwanted threads or "spider web"-like patterns form between separate parts of a print, usually due to excessive retraction or excessively high print temperature.
Solutions:
- Retraction Speed and Distance: Adjust the retraction settings. Too much retraction or too high a speed can worsen stringing; experiment with lower values.
- Lower print temperature: Check that the temperature is not too high, as a lower temperature can reduce the fluidity of the filament.
- Non-printing speed: Increase the print head speed during travel moves so that the filament has less chance of ooze.
Other common problems and solutions
1. Poor first layer and adhesion:
Solutions:
- Make sure you have a nice, flat and clean print bed.
- Adjust the bed temperature and nozzle distance.
- If necessary, use a raft or brim to improve adhesion.
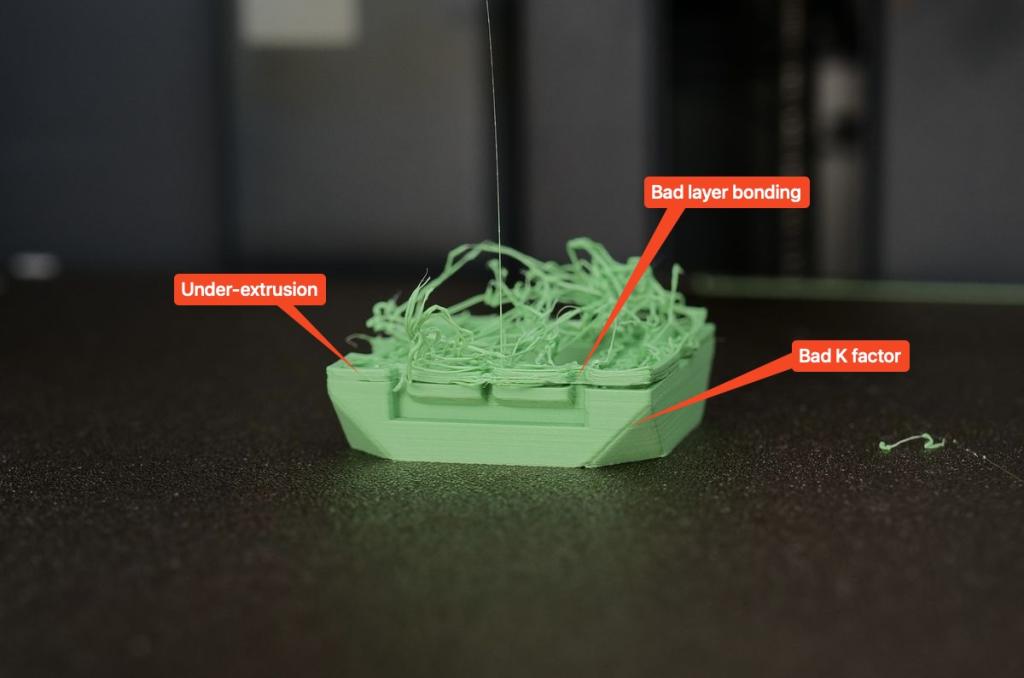
2. Underextrusion:
Solutions:
- Check that the filament is not clogged and that the extruder is functioning properly.
- Slightly increase the extrusion speed or adjust the flow rate.
- Make sure the filament is dry, especially with hygroscopic materials such as Nylon or TPU.
3. Overheating and deformation of layers:
Solutions:
- Reduce the nozzle temperature if necessary.
- Adjust the cooling so that the layers cool faster and do not deform, but avoid overcooling for materials that require heat for optimal adhesion.
4. Blobs and zaps (excessive extrusion at start/stop):
Solutions:
- Change the “seam” settings
- Reduce the extrusion pressure and check the firmware settings.
By carefully adjusting print settings and optimizing the print environment, you can significantly reduce common problems such as warping and stringing. Always test with small prints to fine-tune settings for best results.
Sustainability and Recycling of 3D Printing Filaments
The growing popularity of 3D printing brings not only technological advantages, but also an increasing responsibility for sustainability. Both the choice of filament and the way in which waste material and failed prints are disposed of can have a major impact on the environment. Innovations in recyclable materials and filament recycling technologies offer opportunities to reduce waste and stimulate circular processes.
Biodegradable filaments
Examples and properties:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) is the best-known example of a biodegradable filament, made from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugar cane.
- The filament is industrially compostable, meaning it breaks down under controlled conditions.
- Biodegradable filaments are generally more environmentally friendly, but actual degradability depends on the composting environment.
Advantages:
- Reduction of the ecological footprint through the use of renewable raw materials.
- Suitable for applications where responsible disposal is required after use.
Considerations:
- Home composting is often less effective; industrial composting facilities are usually required to actually break down the material.
- Although PLA is seen as 'greener', recycling remains an important focus to minimize waste.
Recycled filaments and how to recycle filament yourself
Recycled filaments:
- More and more companies are offering filaments that are made entirely or partially from recycled materials, such as old plastic waste or leftover material from previous printing projects.
- These filaments help reduce waste and fit into a circular economy by giving old materials a new life.
- Recycled filaments can have similar properties to their virgin counterparts, although consistency and quality sometimes vary depending on the source materials.
Recycle filament yourself:
- There are extruders on the market that allow you to make your own filament from 3D printing waste, such as failed prints and leftover pieces.
Important steps and points of attention:
- Collection and sorting: Ensure clean collection of residual materials, preferably sorted by type of plastic.
- Cleaning and drying: Remove dirt and moisture, as contaminated material can negatively affect the quality of the new filament.
- Pulverizing and extruding: With a filament extruder, the plastic is pulverized and re-extruded into filament.
- Quality Control: Check the diameter and consistency of the recycled filament; deviations can lead to printing problems.
- Recycling your own filament is an excellent way to reduce material waste, but it requires the right equipment and careful preparation.
By choosing biodegradable and recycled filaments, or by recycling yourself, you as a maker can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly 3D printing world. Experimenting with these sustainable options not only helps to reduce waste, but also stimulates innovation in material technology.
Conclusion
The world of 3D printing filaments offers a wide range of possibilities. From standard materials such as PLA, ABS and PETG to more specialized filaments such as TPU, Nylon and various special variants, each material brings its own properties, advantages and challenges. Choosing the right filament – and the corresponding print settings – is crucial for a successful print and the durability of the final product.
Summary of key points
- Material diversity: There is a wide selection of filaments, each with specific properties. For example, PLA is very suitable for beginners, while ABS and Nylon are more suitable for functional and durable applications.
- Diameter and Compatibility: The choice between 1.75mm and 2.85mm filament plays a big role in print quality. Always check your printer specifications to find the best match.
- Print Settings: Temperature, print speed, bed temperature and cooling are essential factors to prevent problems such as warping, stringing or clogged nozzles.
- Sustainability: In addition to quality, there is increasing attention for environmentally friendly options, such as biodegradable and recycled filaments, and the possibility to recycle filament yourself.
Advice for beginners and advanced users
For beginners, it is wise to start with filaments such as PLA, as they are relatively forgiving and easy to print. Experiment with small prints and adjust the settings step by step to get familiar with your printer.
Advanced users can use the possibilities of materials like ABS, PETG, TPU or Nylon to realize functional, robust and complex prints. In addition, experimenting with special filaments and sustainable options can not only lead to better print results, but also contribute to a more environmentally friendly printing environment.
In short: choose consciously, test carefully and optimize your print settings to get the most out of your 3D printing projects.